The Industrial robot: How does it work?
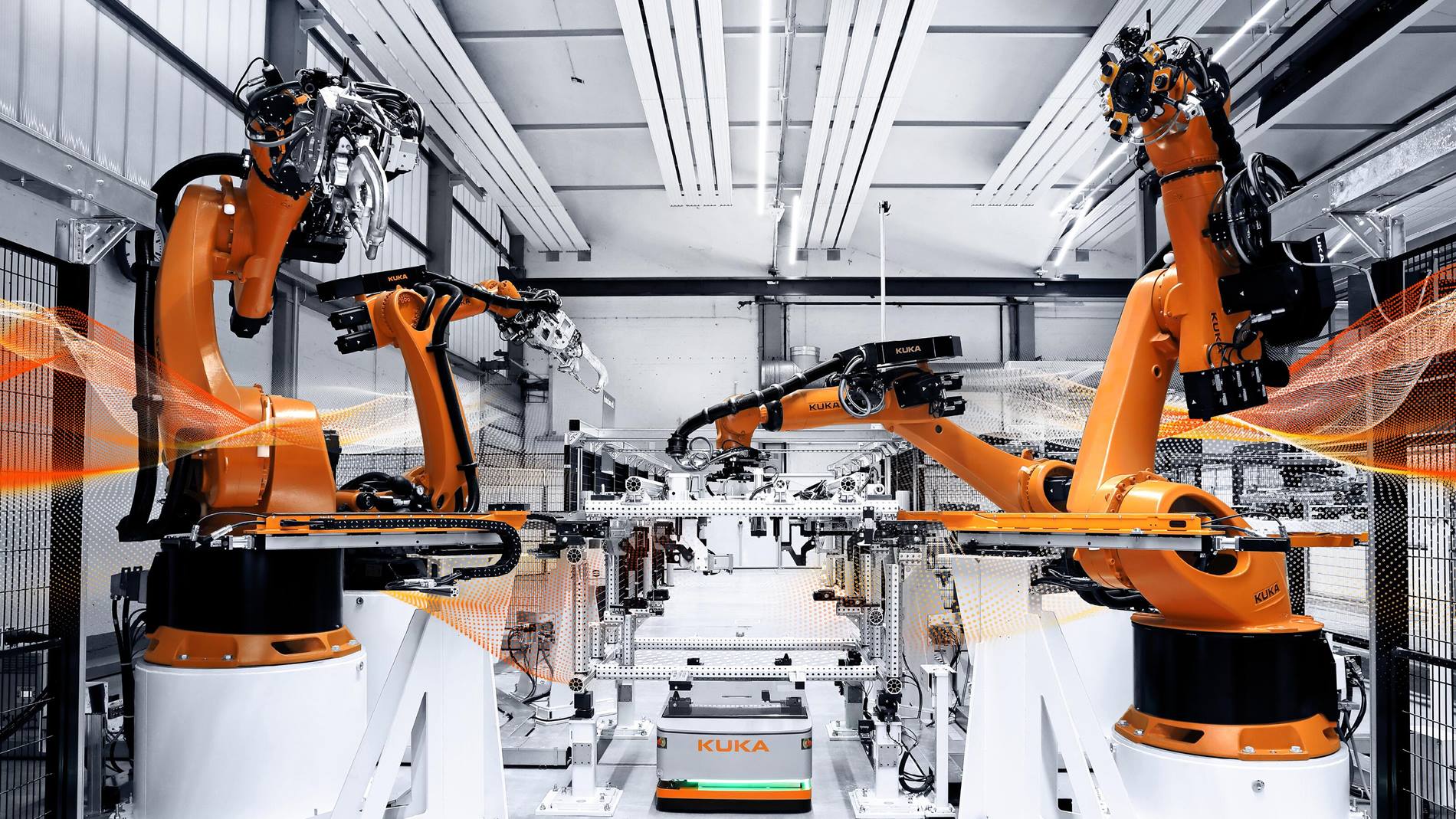
The industrial robot is present in all industries. A programmed system that allows the automation and optimization of production by carrying out various tasks and seems to be the ideal solution for many companies. We will break down how it works and how to choose the best industrial robot.
-
The Cartesian system is a linear robot that moves on three orthogonal axes (X,Y and Z) according to Cartesian data. It is made from a form of linear actuators.
-
A poly-articulated robot can move in a 3D environment thanks to its rotoid joints. It usually has 6 axes.
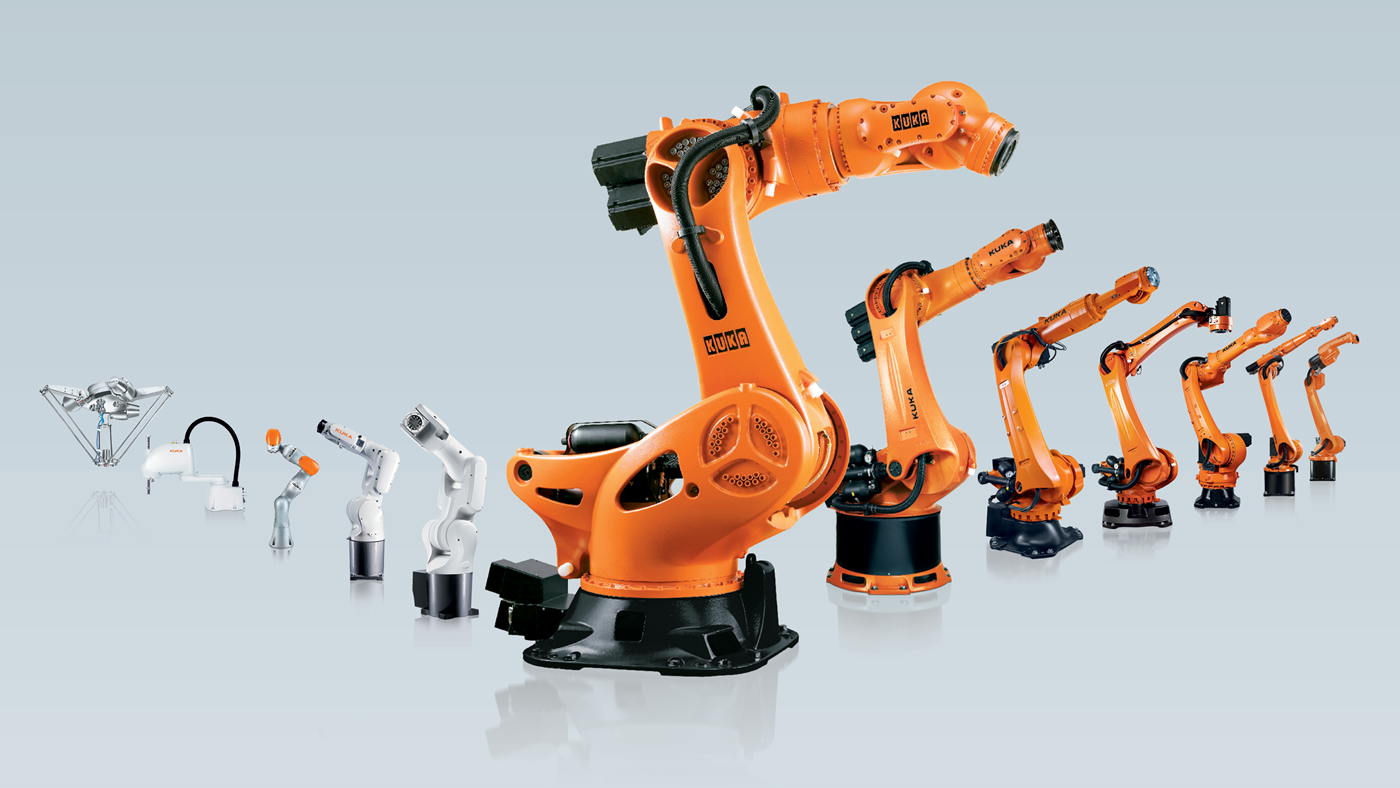


A robotic system has three major components:
-
A mechanical part: the arm itself which is composed of motors on each axis.
-
An electronic part: the control cabinet with its central unit which ensures the servo control, its sensors and speed variators.
-
A computer part: in the form of a specific programming language that allows the robotic machine to be controlled by linking it to its user and its environment. This computer part includes a calculator that converts the coded motor data into Cartesian values.
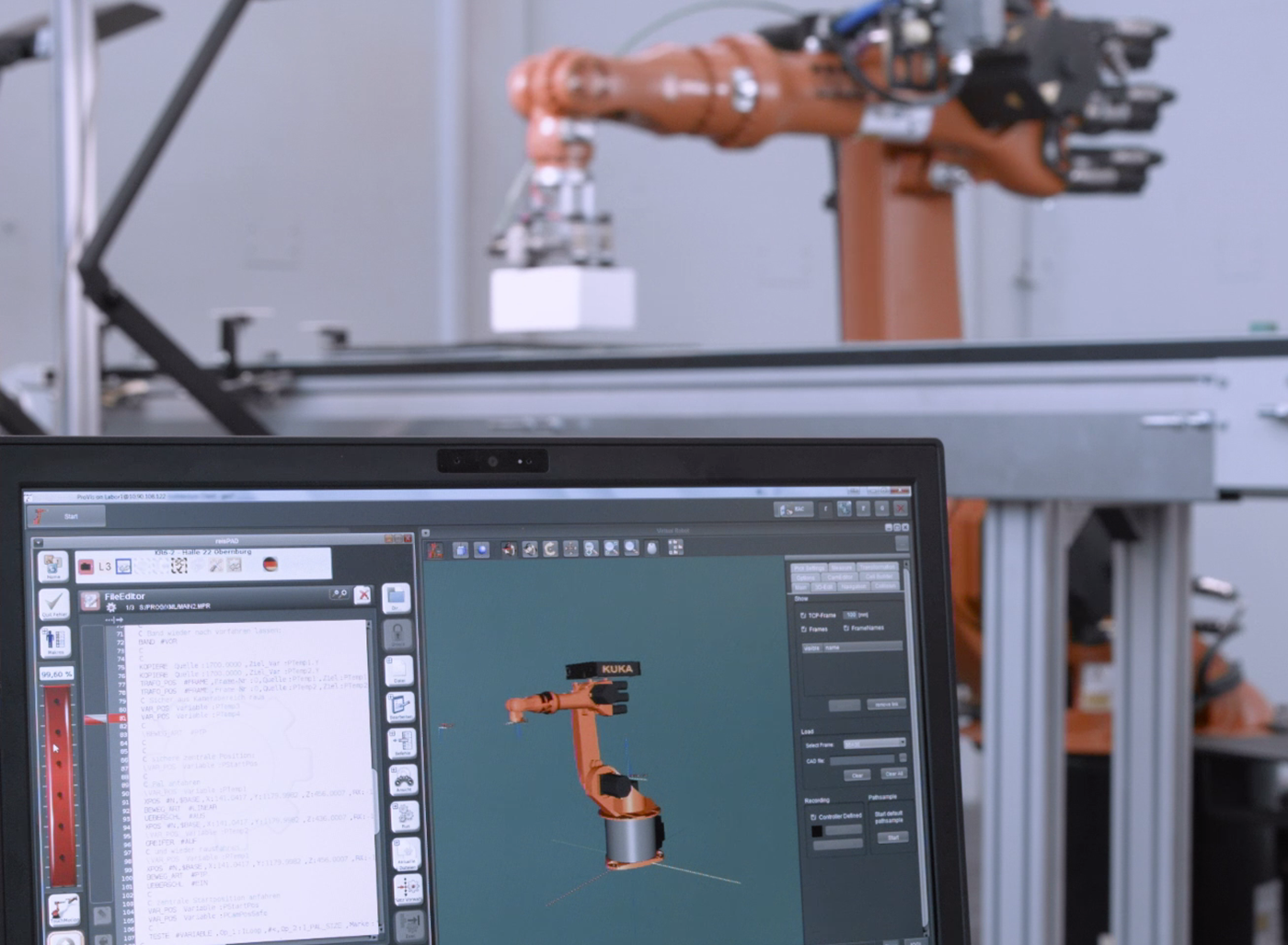
It is the programming that allows the elements to link between them and to make a naked robot, a tool for the automation of industrial operations. There are three methods:
-
Programming by learning is the first method to be developed. It consists in creating trajectories by memorizing Cartesian coordinates. This will determine the robot's working and passing positions. This method is performed directly on the android via the control box, the smartPAD at KUKA, or by manual guidance with suitable tools, such as the ready2_pilot.
-
The calculated method came next. It consists of determining the position of the points using formulas based on the first point defined.
-
A third method appeared, modifying the practice of the first two. The off-line programming consists in creating and simulating the trajectories on an off-line programming software. Thus, the working environment of the robotic solution is recreated and allows a large panel of tests.

What is the purpose of an industrial robot?
-
Assembly and mounting
-
Palletizing
-
Material Handling
-
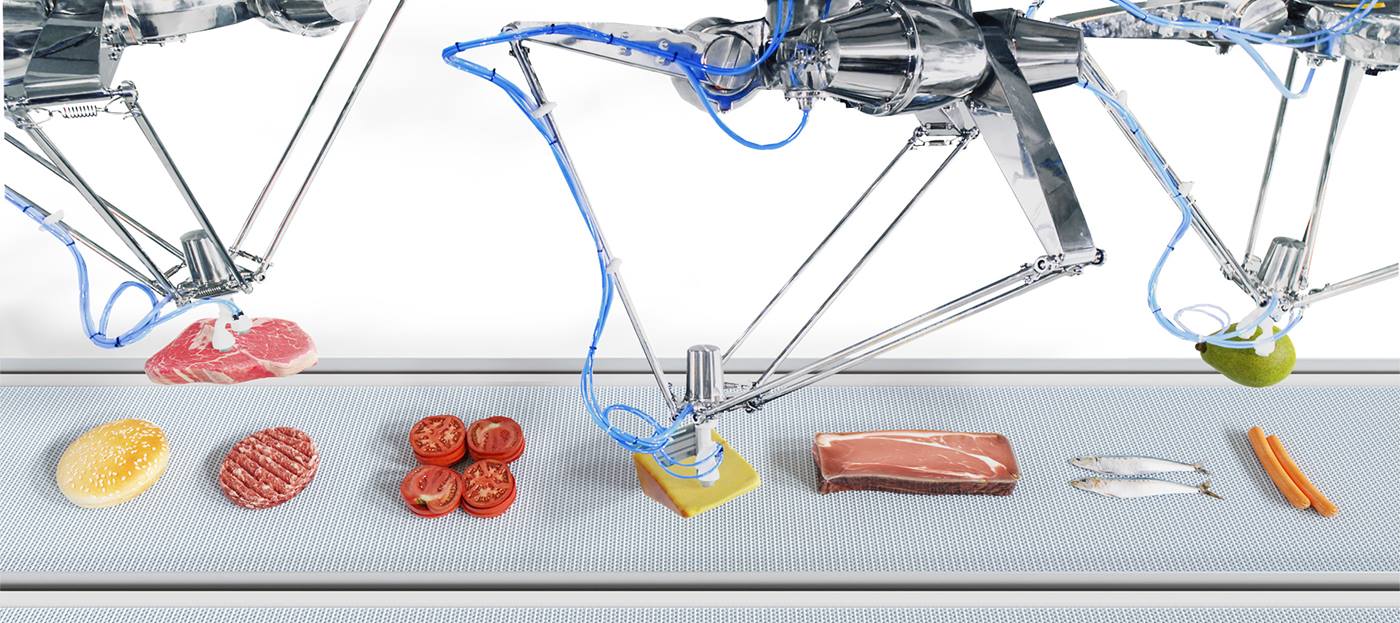
Packaging
-
Machining
-
Foundry and forging
-
Robotic Welding and cutting of all materials
-
Pick and place
-
Die casting
-
Welding

Advantages of use
Industrial robots bring a speed of execution in a manufacturing environment superior to the human and a durable precision over time. Factoring in their high accuracy levels, industrial robots are capable of high quality production and executing more precise and reliable processes. A high product quality results in a decrease in time taken for quality control checks to determine if the products are of the desired standards.
Thus, many advantages result from the use of automation technology:
-
Improvement of the output
-
Maximization of production
-
Optimization of quality
-
Almost perfect and repeatable precision
-
Reduction of risks for employees
-
Improved working conditions: less RSI
-
Certainty of consistency of rate and process
-
Increased flexibility
How to choose the best robot system?
The best robot will be the one that best meets the specific needs of a manufacturing project. To do so, it is important to know some key criteria as there are different types of robots:
-
The task to be automated
-
The required reach
-
The load (the weight of the part to be carried...)
-
The cycle time
-
The working environment
When integrating an industrial robot, a classic or collaborative robot, safety is a necessity and therefore it is essential to perform a risk analysis beforehand. Especially cobots that work in the same environment as humans in order to combine human capabilities with the efficiency of machines require a lot of safety precautions. Once you have these elements in mind, you can carry out research or use this tool which will calculate the industrial automaton best suited for your needs.
Alternatively, you can contact our experts directly for personalized support. In short, there is no such thing as the best robot, but robotic arms exist for all situations and applications.