EV Suppliers Opt for Experience When Integrating Robot-Based Friction Stir Welding
No industry sector drives the use of friction stir welding (FSW) more than automotive Electric Vehicle (EV) manufacturing, primarily for the production of battery storage trays as well as other vehicle components.
No industry sector drives the use of friction stir welding (FSW) more than automotive Electric Vehicle (EV) manufacturing, primarily for the production of battery storage trays as well as other vehicle components. However, many companies now producing EV components are new to the industry. When it comes to integrating the FSW process into their operations, they often look to suppliers like KUKA that have decades of both robotic and FSW experience to make the integration as smooth and cost-efficient as possible.
To maximize their competitiveness, automotive manufacturers generally seek to include certain strategic elements in their operations. Single-source supply simplifies their purchasing efforts and provides opportunities to generate cost savings. Process reliability is an essential factor in maintaining and growing production output. Manufacturing processes should be scalable to enable economical response to changing business conditions. Manufacturers also need up-to-date training resources to assure their staff has the knowledge and skills required to maximize production efficiency.
KUKA helps manufacturers achieve those strategic goals. Combining its longtime experience in robotic technology and its development efforts in the relatively recent FSW techniques, KUKA’s Robot-Based 3D Friction Stir Welding systems give automotive manufacturers an integrated approach to fulfilling the new demands of EV production.
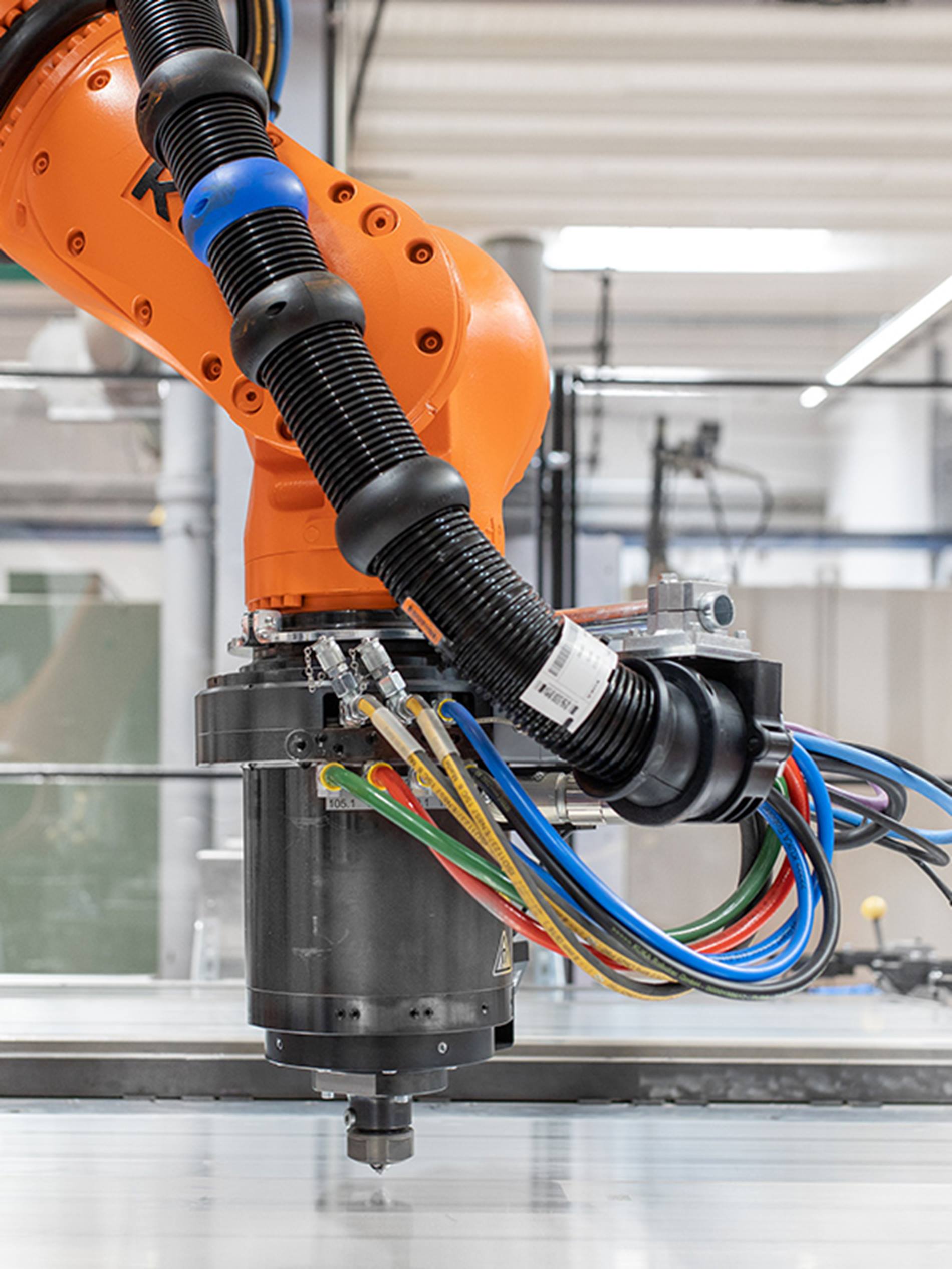
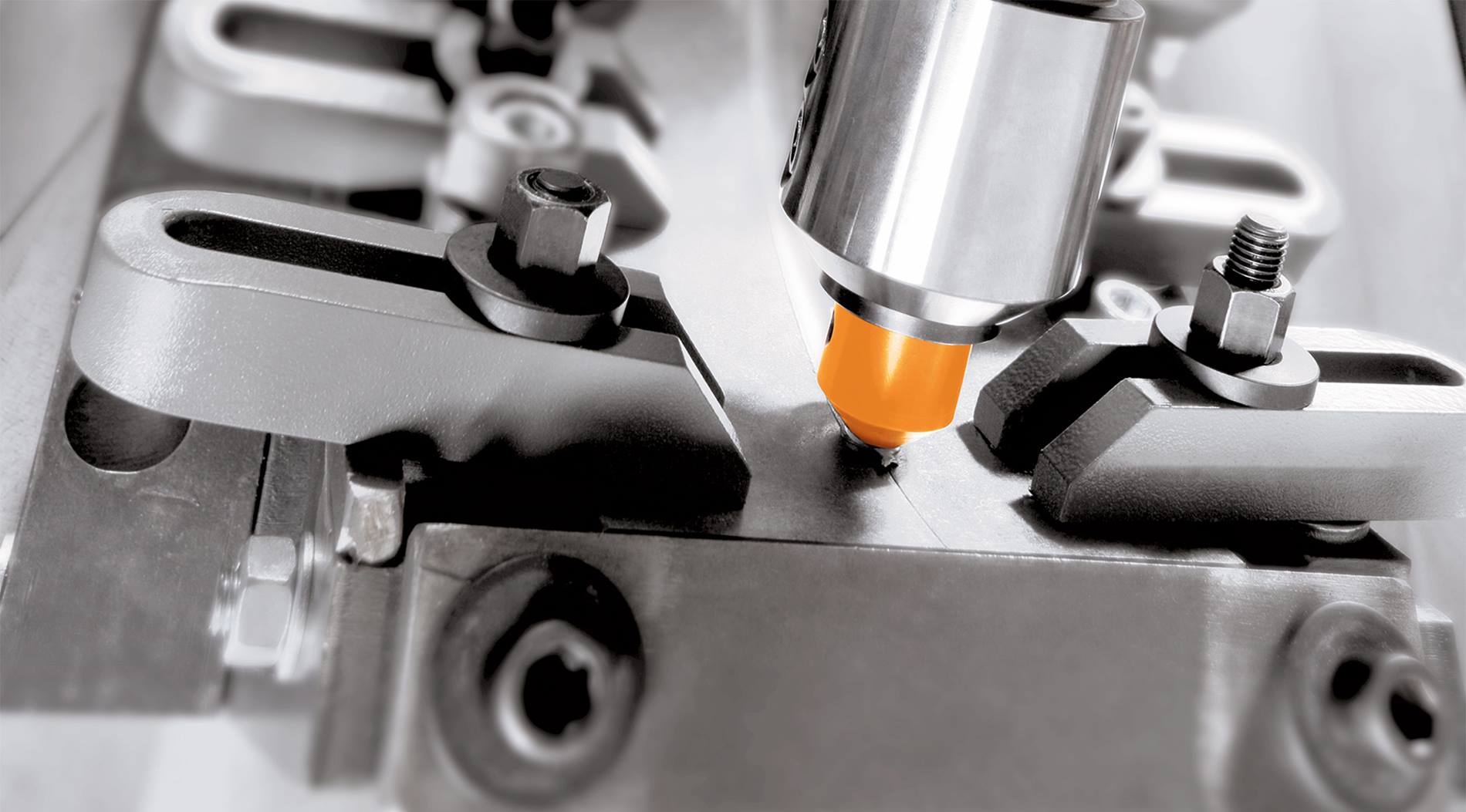
FSW is a unique and effective manufacturing method. In the process, a rotating tool with a central pin generates heat as it spins and moves along a joint between two components, plasticizing the materials being joined. The resulting bond is defect-free and strong, uses no filler material and requires little post-processing. FSW joins materials without actually melting them, minimizing any heat-affected zone that can compromise a joint’s strength and cause part distortion. The FSW process is also safe and not accompanied by the arcs, toxic fumes and molten spatter produced by conventional welding.
The singular characteristics of FSW are prompting manufacturers to apply it in joining materials that previously have been difficult or even impossible to weld reliably and economically with traditional welding techniques. Typical problem jobs include joining thin and thick gauge aluminum components, copper alloys or dissimilar materials.
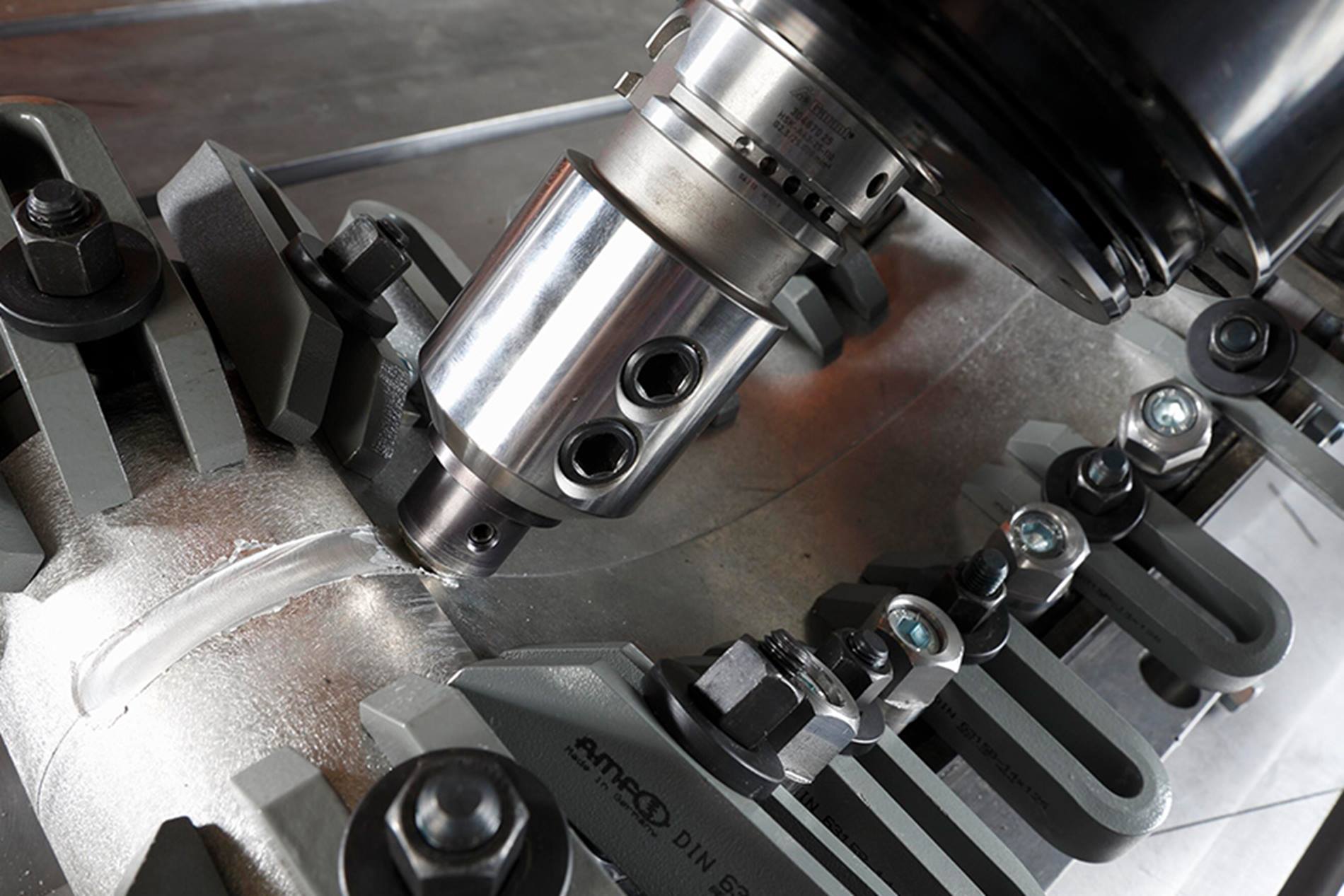
Manufacturing housings for electric vehicle (EV) batteries is a prime FSW application. The housings generally are large, sometimes encompassing the length and width of a vehicle’s chassis. The housings have to feature sealed internal channels to transport liquid for battery cooling. Low weight is a major priority. Manufacturers now can conventionally machine the channels and then apply FSW to close and seal complex 3D seams on the housings, achieving excellent sealing integrity while minimizing weight and eliminating the operational and environmental challenges of conventional welding.

KUKA robotic FSW systems utilize six-axis robots that provide modularity and flexibility needed to carry out 2D and 3D welding tasks. The systems represent scalable solutions and provide high efficiency (up to 95 percent) via use of multiple workstations that permit simultaneous welding by several robots for complex larger components. KUKA path calibration technology produces path accuracy up to 0.5 mm.
The company’s KUKA Cell4_FSW module is engineered for use with the KUKA KR500 R2830 FORTEC MT robot with a KR C4 controller and an FSW 3 spindle. The KR 500 robot provides 6-axis flexibility with 2,830 mm - 3,326 mm of reach, load capacity of 340 kg - 500 kg, and repeatability of 0.08 mm. The integrated FSW spindle enables force-controlled FSW processes. The Cell4_FSW module can be employed with with single or dual KR robots, and the module is Industry 4.0 ready, with interfaces based on OPC UA for easy data exchange.
KUKA’s PCD (Process Control and Documentation) system provides 100% real-time process monitoring for continuous-path FSW processes as well as tracking of numerical and graphical parameters. It also delivers component and product data management and export, process diagnostics, electronic documentation and archiving of all process data. Offering connectivity to cloud systems, KUKA PCD ensures high productivity and traceable quality and data transparency. KUKA provides comprehensive training and support for all aspects of its FSW systems, from implementation and operational techniques to data gathering and management.
FSW methods provide a specialized blend of efficiency and productivity in a growing range of contemporary applications. New product technologies such as EV transportation and introduction of product designs requiring bonding of difficult-to-weld and dissimilar materials are prompting increased interest in the uniquely capable process of KUKA friction welding.


